
Surfactants are characterized based on their hydrophilic group, that is, ionic, nonionic, and zwitterionic. It dissolves in surfactant, detergents, which are amphipathic (hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head) in nature, very much similar to phospholipid membranes. This can be weakened to open the cell wall, by applying mechanical force exerted during grinding along with CTAB buffer or liquid nitrogen.Ĭell membrane lies next to the cell wall and cellulose and is composed of a diverse set of phospholipid molecules and proteins.
The plant cells enclose themselves in complex polysaccharide cell wall, of which cellulose is a major constituent, which is crystalline in nature, due to chain-like structure and intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The role of various chemicals involved in CTAB extraction method has been described in the present communication. The majority of the protocols developed for DNA extraction are modified versions of hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) extraction. The plant DNA is extracted by either CTAB-based or sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-based methods. The basic principle of DNA isolation is disruption of the cell wall, cell membrane, and nuclear membrane to release the highly intact DNA into solution followed by precipitation of DNA and removal of the contaminating biomolecules such as the proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, phenols, and other secondary metabolites by enzymatic or chemical methods. Generally, leaf samples contain large quantities of polyphenols, tannins, and polysaccharides. The main objective of various DNA isolation methods is development of relatively quick, inexpensive, and consistent protocol to extract high-quality DNA with better yield. If liquid nitrogen is unavailable, CTAB buffer can be used directly or prewarmed for grinding. Generally fresh leaves aged 15–20 days are preferred for plant tissues (fresh, freeze-dried, or frozen in liquid nitrogen) and usually ruptured by mechanical force in pestle and motor or TissueLyser. These contaminants can be removed during extraction by standardizing basic DNA extraction protocol. The amount of these components varies according to plant species, plant part used, environmental condition, and growth stage and it is very problematic when isolating DNA. For example, cereals are rich in carbohydrates whereas medicinal plants are rich in the polyphenols wherein stressed plants have higher polyphenols. Maintaining yield and quality of DNA during plant DNA extraction is one of the difficult tasks compared to that of animals, because of its rigid cell wall, which is made up of cellulose along with other variable levels of chemical components such as polysaccharides, polyphenols, proteins, and lipids that act as a contaminant during DNA extraction.
#Dna sugar phosphate backbone code#
#Dna sugar phosphate backbone free#
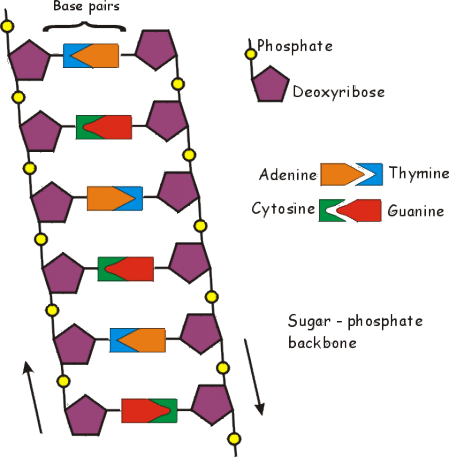
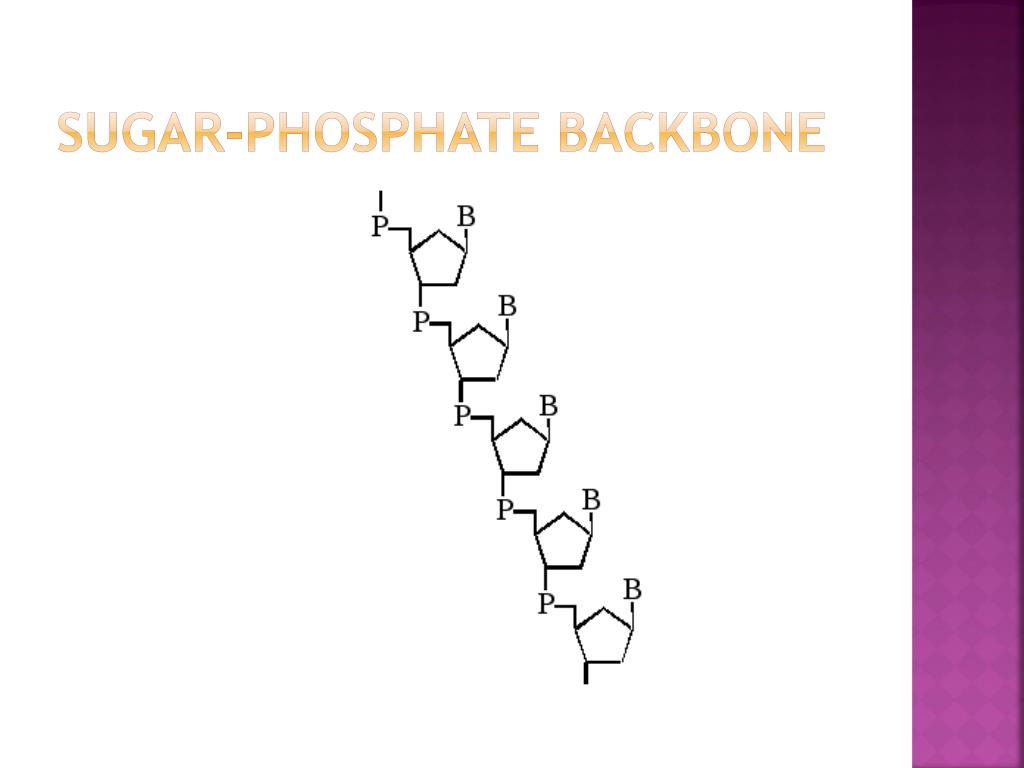
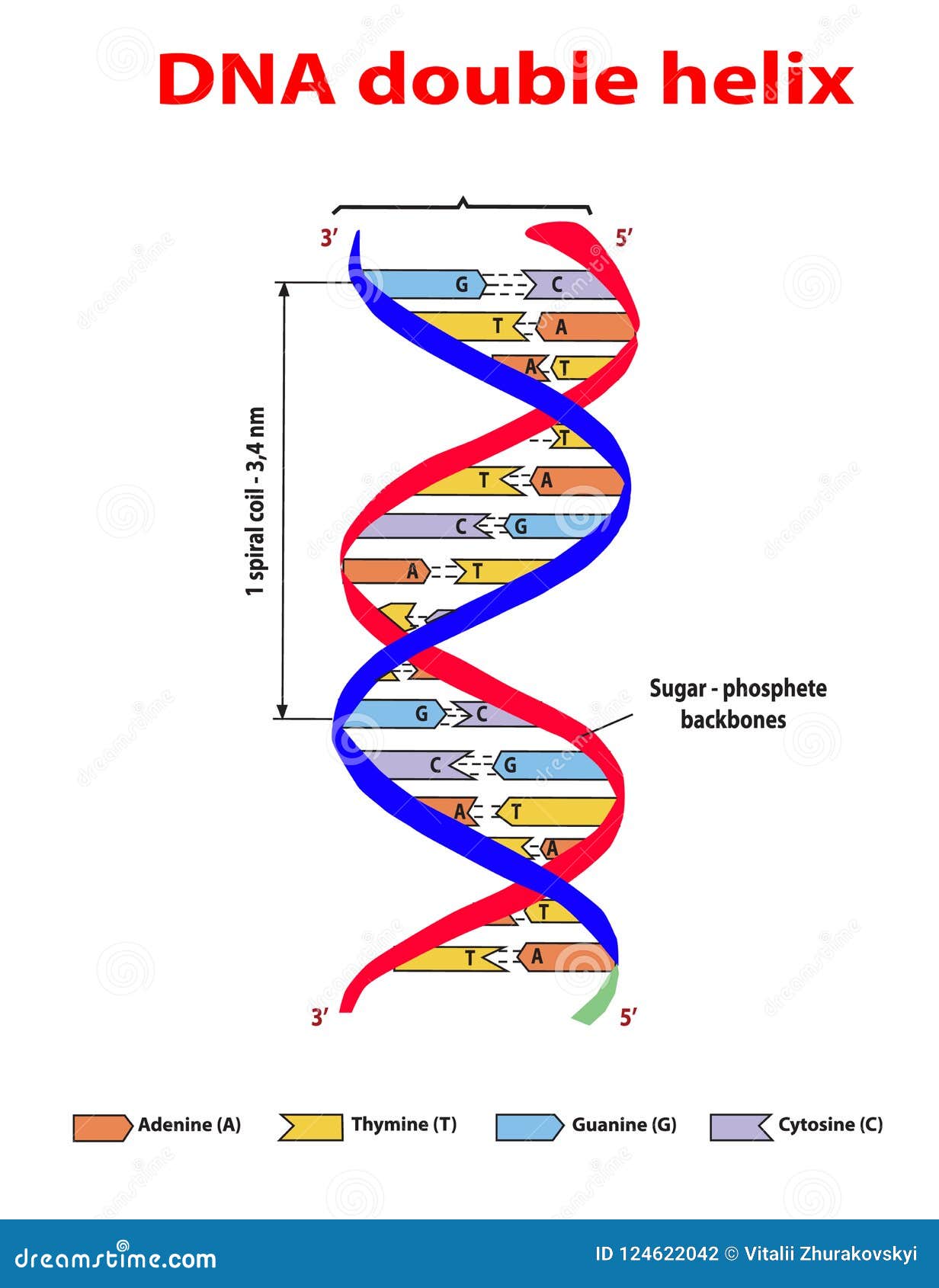
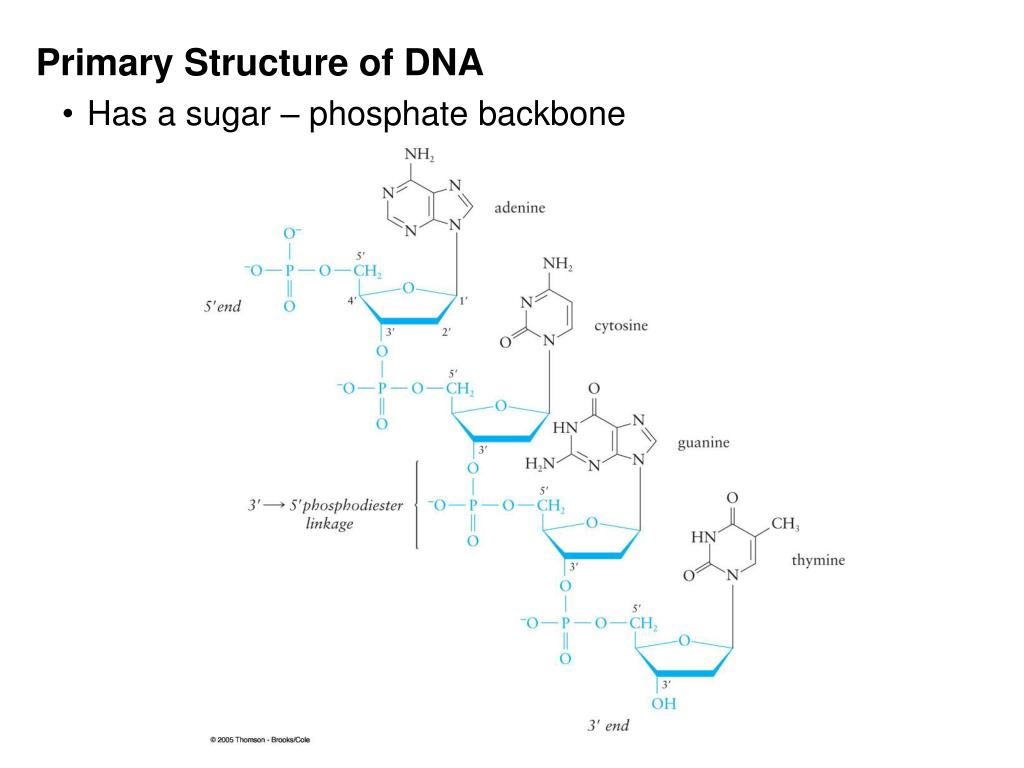
The 5ʹ end is the one where carbon #5 is not bound to another nucleotide the 3ʹ end is the one where carbon #3 is not bound to another nucleotide and has a free hydroxyl group. (c) The direction of each strand is identified by numbering the carbons (1 through 5) in each sugar molecule. (b) The two DNA strands are antiparallel to each other. (a) The sugar-phosphate backbones are on the outside of the double helix and purines and pyrimidines form the “rungs” of the DNA helix ladder. \):Watson and Crick proposed the double helix model for DNA.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
